Different Kinds of Genius: Exploring the Diverse Facets of Exceptional Intelligence
Introduction
The idea of genius has intrigued people for generations. Often linked to rare brilliance in science, art, or music, genius actually appears in countless shapes. This article surveys the broad landscape of exceptional intelligence, illustrating how remarkable ability can surface in many areas of life.
The Traditional View of Genius
Classic portrayals depict genius as an isolated figure blessed with an inborn, almost mystical gift. Rooted in Romantic ideals, this image suggests that a chosen few arrive in the world pre-equipped for greatness. Yet such a narrow lens overlooks the varied paths by which extraordinary talent emerges.
The Many Faces of Genius
1. Intellectual Genius
Intellectual genius shows up in profound reasoning, inventive problem-solving, and theoretical insight. Scientists, mathematicians, and philosophers who reshape how we understand reality exemplify this form of brilliance.
2. Artistic Genius
Artistic genius reveals itself through original expression in painting, music, literature, and other creative fields. These creators translate emotion and imagination into works that resonate across cultures and eras.
3. Athletic Genius
Athletic genius combines physical grace with strategic insight, allowing individuals to push the boundaries of speed, strength, coordination, and endurance. Mastery in sport often stems from both natural aptitude and relentless refinement.
4. Social Genius
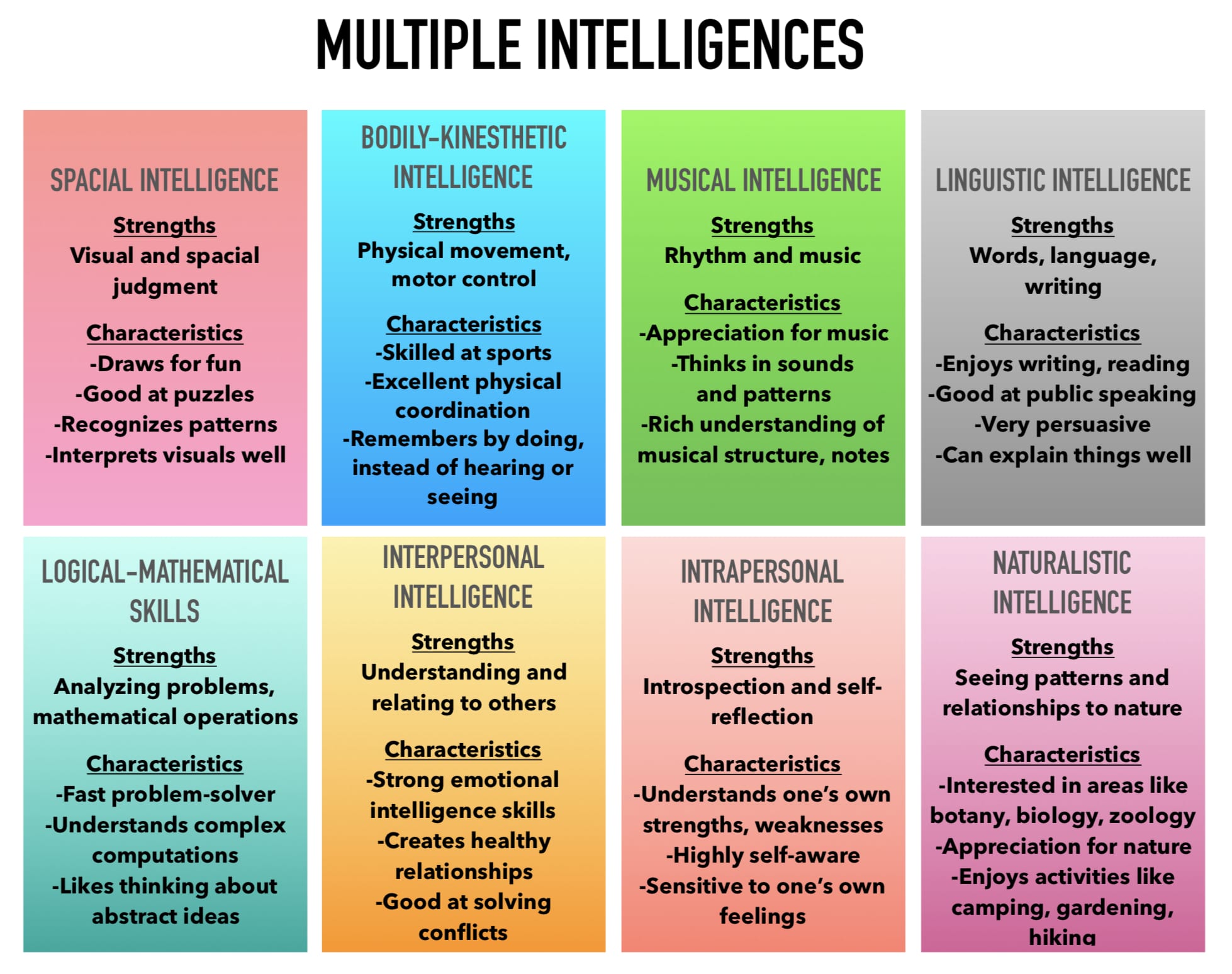
Social genius lies in reading complex interpersonal dynamics and guiding groups toward shared goals. Skilled negotiators, inspiring leaders, and compassionate mediators display this talent for shaping constructive human interaction.
The Role of Environment and Nurture
Exceptional ability rarely develops in isolation. Surroundings, guidance, and sustained effort interact with innate potential to cultivate high achievement.
1. Early Exposure
Access to rich stimuli in childhood—books, instruments, open-ended play—can ignite lifelong curiosity and lay the groundwork for later excellence.
2. Mentorship
Knowledgeable mentors accelerate growth by offering feedback, encouragement, and opportunities that might otherwise remain out of reach.
3. Practice and Persistence
Deliberate practice over months and years sharpens skills, turning raw promise into polished expertise. Consistency, reflection, and incremental challenge are key ingredients.
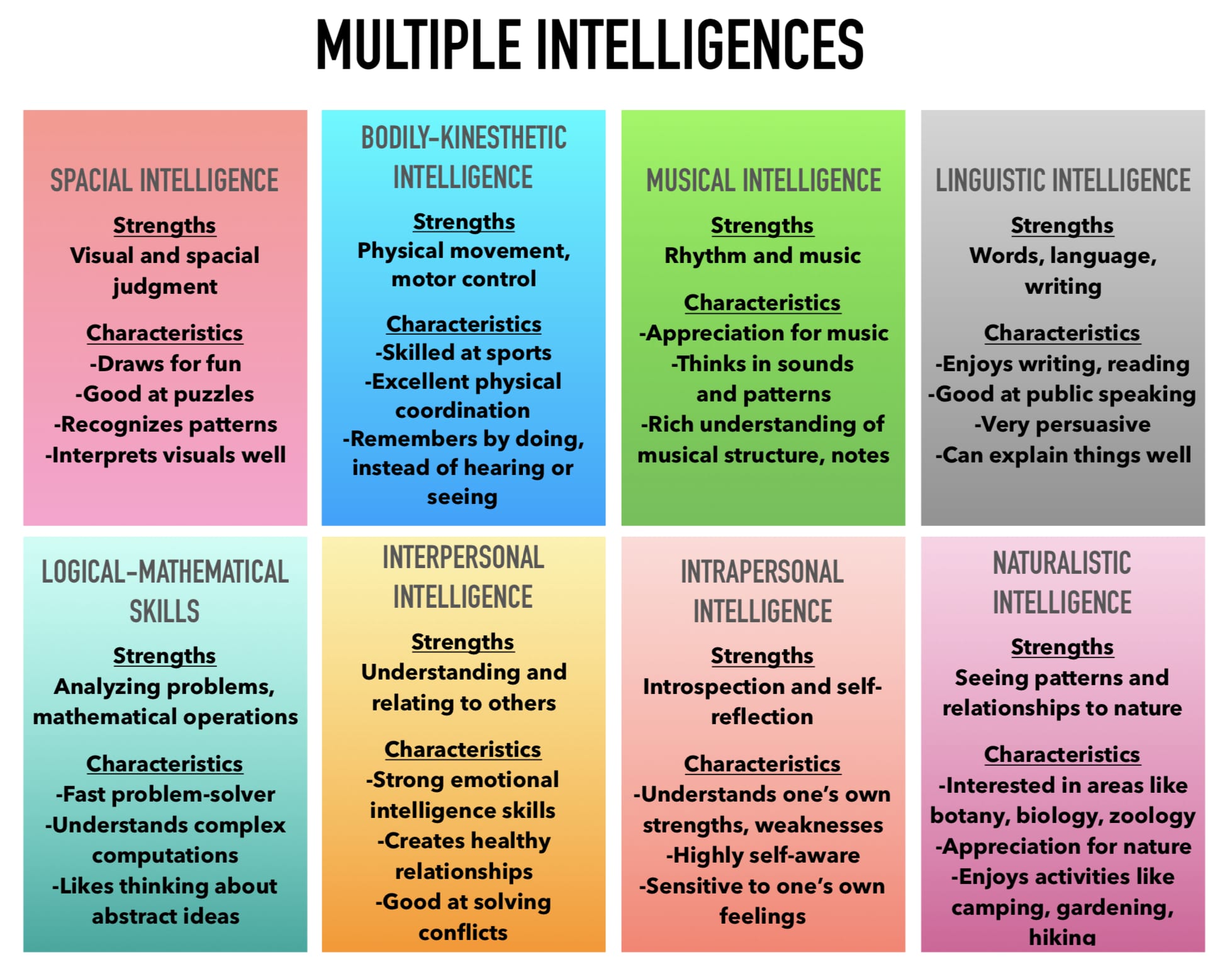
The Importance of Recognizing Different Kinds of Genius
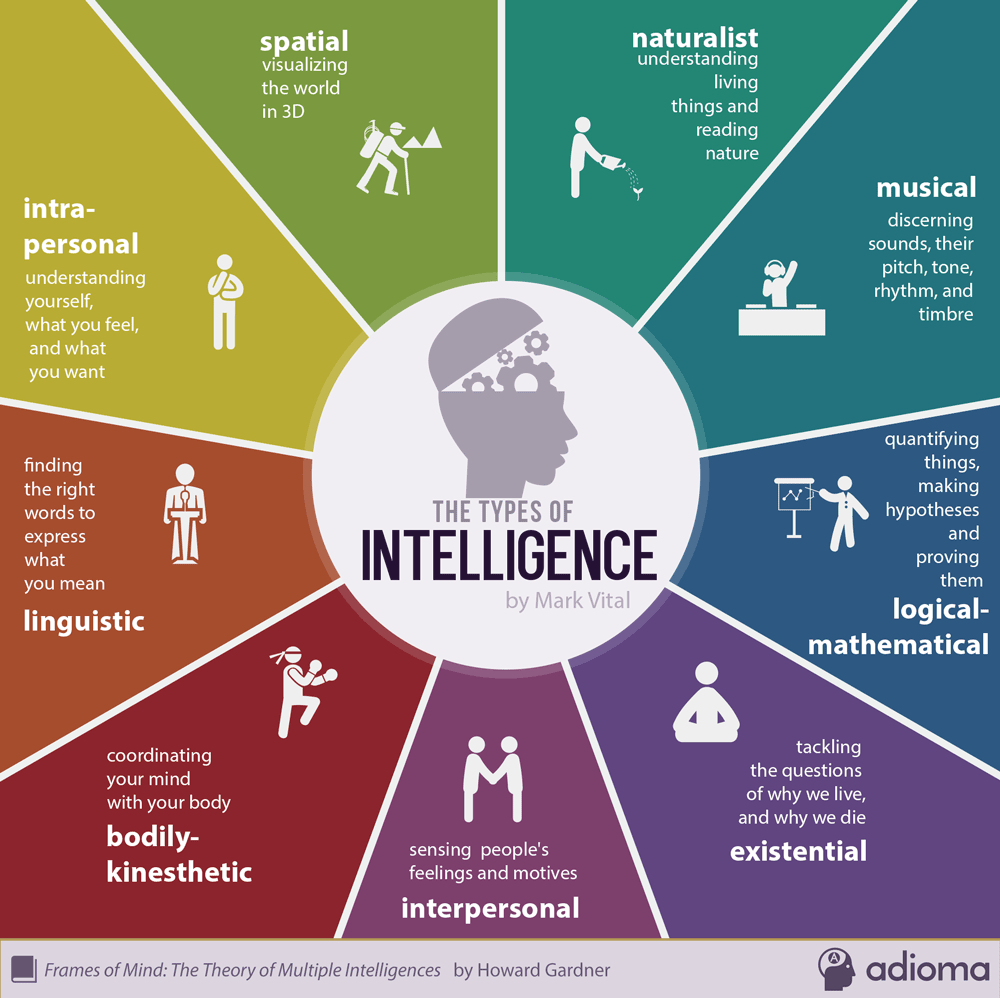
Valuing diverse expressions of talent benefits individuals and society alike.
1. Encouraging Diversity
When varied strengths are celebrated, more people feel empowered to pursue their unique interests, enriching the cultural and intellectual fabric of communities.
2. Promoting Well-being
Acknowledging multiple forms of excellence fosters self-confidence and mutual respect, supporting mental health and social cohesion.
3. Enhancing Education
Understanding that students shine in different ways helps educators design flexible curricula that nurture each learner’s potential.
Conclusion
Genius is not a single, elusive trait reserved for the few; it is a spectrum of exceptional capacities that can emerge in any domain. By appreciating the interplay of innate inclination, supportive environments, and dedicated practice, we create conditions where diverse talents can flourish. Recognizing the many faces of genius invites everyone to explore their own capacity for remarkable contribution.