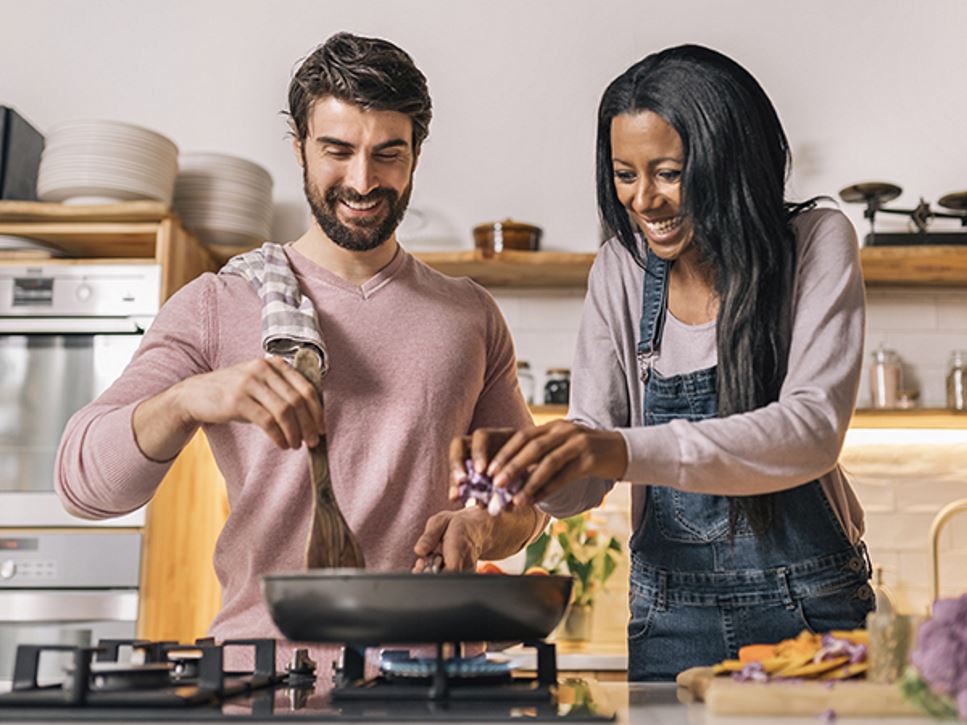
The Art and Science of Cooking: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
Cooking, an age-old craft, has matured into a discipline that blends imagination with exactness. It is more than sustenance; it is a way to craft experiences that delight the senses and nurture the body. This article journeys through cooking’s many dimensions, from its earliest days to its present forms, examining the methods, ingredients, and cultural meanings that turn it into a shared global tongue.

The Historical Evolution of Cooking
Ancient Beginnings
From humanity’s first fires onward, cooking has shaped civilization. Harnessing flame softened food, improved safety, and released new flavors. Simple tools and growing knowledge of heat gradually widened the culinary horizon.
The Middle Ages and the Renaissance
Trade routes and cultural exchanges introduced new seasonings and techniques to medieval kitchens. The Renaissance spurred further creativity, as cooks refined recipes and embraced bolder combinations.
The Science Behind Cooking
Heat Transfer
At its core, cooking moves energy into ingredients. Conduction passes heat through direct contact, convection circulates hot air or liquid, and radiation delivers energy through invisible waves. Each pathway influences texture and taste in distinct ways.

Chemical Reactions
Heat triggers transformations such as the Maillard reaction, where amino acids and sugars meet to create color, aroma, and depth. Similar processes caramelize sugars, firm proteins, and soften fibers, turning raw components into harmonious dishes.
Techniques and Methods
Sautéing
A swift technique using minimal fat over lively heat, sautéing seals in moisture and heightens flavor. It suits tender vegetables, thin cuts of meat, or delicate seafood that cook within minutes.
Baking
Surrounding food with steady, dry heat, baking coaxes structure and golden crusts from doughs and batters. Even temperatures allow breads, pastries, and casseroles to cook through while developing appealing surfaces.
Boiling
Submerging ingredients in bubbling liquid delivers rapid, uniform heat. The method softens grains, pastas, and vegetables, forming the base for soups, stews, and countless comfort foods.

Ingredients and Flavors
Herbs and Spices
Leaves, seeds, bark, and roots supply layers of aroma and color. Fresh herbs lend brightness, while dried spices offer concentrated warmth, allowing cooks to balance and personalize every plate.
Fats and Oils
Beyond conveying heat, fats carry flavor and create luscious mouthfeel. Butter, plant oils, and rendered fats each bring distinct characters, enriching sauces, crisping edges, and uniting seasonings.
Cultural Significance of Cooking
National Cuisine
Kitchens mirror identity: one region may celebrate bold tomato sauces, another prizes subtle broths and seasonal produce. Such preferences tell stories of climate, history, and shared memory, inviting newcomers to the table.

Culinary Traditions
Recipes handed down through generations preserve collective knowledge. Festive breads, ritual stews, or everyday spice blends link past and present, anchoring communities in familiar taste and aroma.
Modern Trends in Cooking
Molecular Gastronomy
By investigating physics and chemistry, innovative chefs craft surprising textures—foams, gels, and pearls—that challenge expectations while respecting flavor. The movement highlights curiosity and precision alike.
Plant-Based Diets
Interest in vegetables, legumes, and grains continues to rise, inspiring new techniques for coaxing umami from mushrooms, creaminess from nuts, and crispness from baked chickpeas, proving that vibrant meals need not rely on animal products.
Conclusion

Cooking remains a living fusion of creativity, inquiry, and heritage. From ancient hearths to contemporary labs, it evolves constantly, offering limitless room for discovery. By mastering heat, honoring tradition, and welcoming innovation, anyone can prepare food that comforts, excites, and connects.
The value of cooking rests not only in pleasure but also in its contribution to well-being. As palates expand and knowledge deepens, emerging practices promise to make the kitchen a place of health, sustainability, and shared joy.
Recommendations and Future Research
Cooks of every level benefit from experimenting with unfamiliar techniques and produce. Studying how different preparations affect nutrients can guide choices toward balanced, wholesome meals.
Exploring cooking’s influence on mood and community, alongside eco-friendly methods and ingredients, may inspire responsible habits that nourish both people and planet for years to come.