The Art and Craft of Belgian Chocolate Makers
Introduction
Belgian chocolatiers have earned worldwide admiration for their refined approach to chocolate making. Rooted in a centuries-old heritage, this craft blends time-honored methods with creative flair. This article explores the distinctive techniques, cultural resonance, and international influence of Belgium’s chocolate tradition.

The Historical Context
Chocolate production in Belgium began to flourish several centuries ago, when the first tasting rooms opened in Brussels. The nation’s close ties with early European trade routes allowed cocoa culture to take hold quickly. Generations of artisans have since perfected their skills, building a reputation that still sets the standard today.
The Unique Techniques of Belgian Chocolate Makers
Several practices distinguish Belgian chocolate from other varieties:
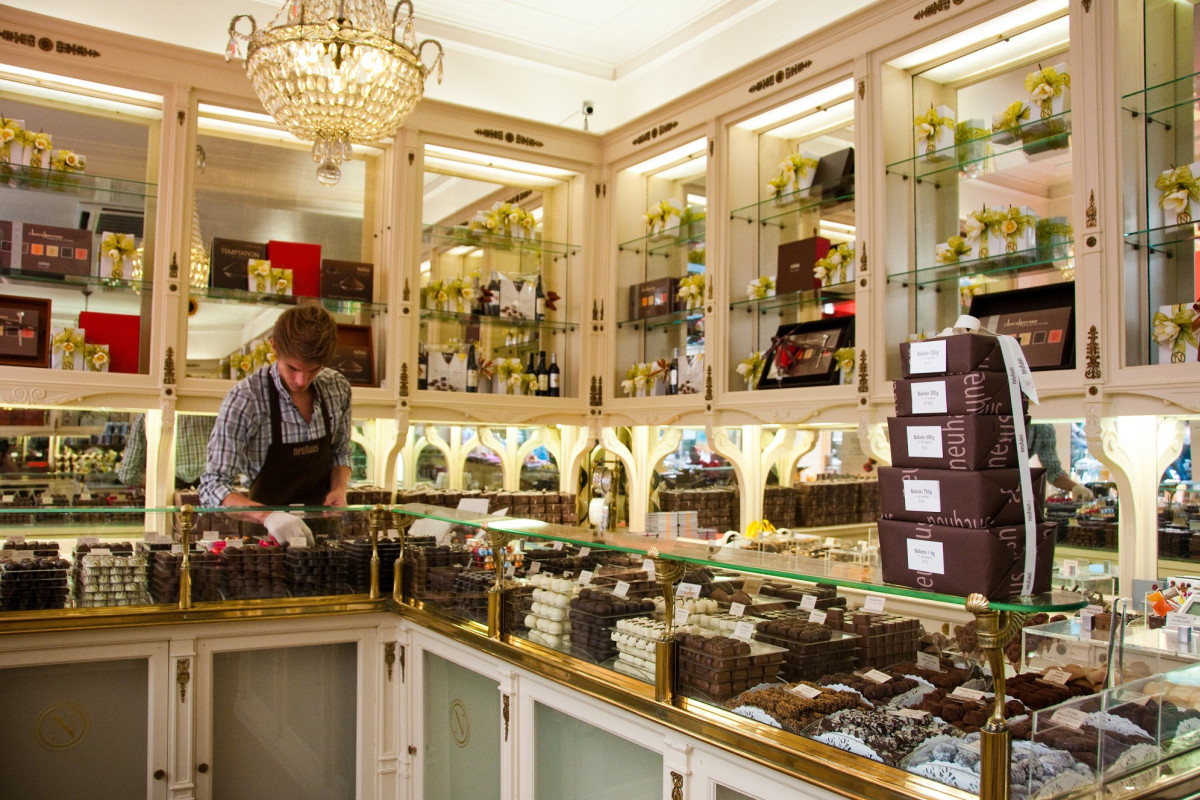
Origin of Ingredients

Producers pay close attention to cocoa sourcing, selecting premium beans from renowned growing regions. Each batch is evaluated for aroma and flavor before it enters the workshop.
Traditional Production Methods
Many houses still rely on slow stone grinding, a gentle process that protects delicate cocoa notes. Extended conching further refines texture and releases hidden nuances.
Artisanal Craftsmanship
Hand tempering, careful molding, and meticulous finishing remain central to the process. Such personal oversight guarantees the glossy finish and balanced taste for which Belgian chocolates are famous.

The Cultural Significance of Belgian Chocolate
More than a sweet treat, chocolate is woven into daily life and national pride. Town centers teem with boutique shops, seasonal fairs celebrate cocoa, and songs even toast the “land of pralines.”
Chocolate Festivals
Throughout the year, festivals invite visitors to sample truffles, watch live demonstrations, and meet the makers. These gatherings keep local heritage alive while welcoming new enthusiasts.
Chocolate in Art and Literature

From surrealist canvases to contemporary novels, chocolate often appears as a symbol of indulgence and identity. Its recurring presence underscores how deeply the craft resonates across creative fields.
The Global Impact of Belgian Chocolate
Belgian chocolates travel far beyond national borders, shaping tastes and industry standards worldwide.
Export Market
Shipments reach well over a hundred countries, making the nation one of the leading suppliers of premium chocolate.

Influence on Chocolate Industry
By championing quality and consistency, Belgian makers have inspired peers everywhere to refine recipes, upgrade sourcing, and invest in staff training.
The Future of Belgian Chocolate
Looking ahead, the sector balances respect for tradition with responsiveness to modern demands.
Sustainable Practices

More producers now partner with certified farms, support reforestation, and monitor supply chains to secure ethical cocoa for the long term.
Innovation
New flavor pairings, reduced-sugar options, and functional ingredients such as plant proteins illustrate how heritage brands stay relevant to health-minded consumers.
Conclusion
Centuries of passion, precision, and creativity have made Belgian chocolate an international benchmark. As sustainability and innovation guide the next chapter, this beloved craft is poised to delight future generations just as profoundly as it does today.

References
– National Chocolate Museum, Brussels.
– Belgian Chocolate Council publications.
– Culinary Journeys: Chocolate Edition, Food & Wine.
– Global Market Trends in Premium Chocolate, International Journal of Gastronomy.
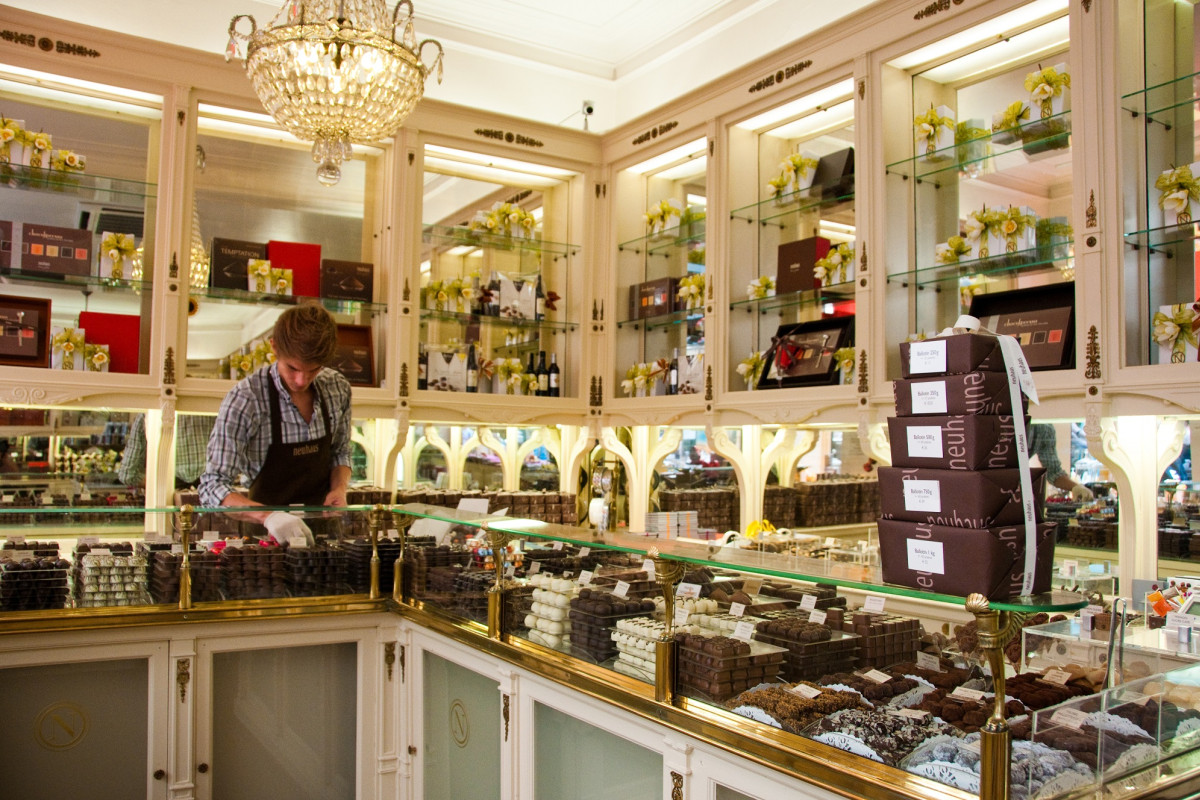

Recommendations and Future Research
To strengthen the industry further, stakeholders may consider:
1. Funding studies on novel flavor profiles and potential wellness attributes of cocoa.
2. Expanding farmer support programs that reinforce environmental and social standards.
3. Sharing technical expertise with emerging chocolatiers to widen market access.
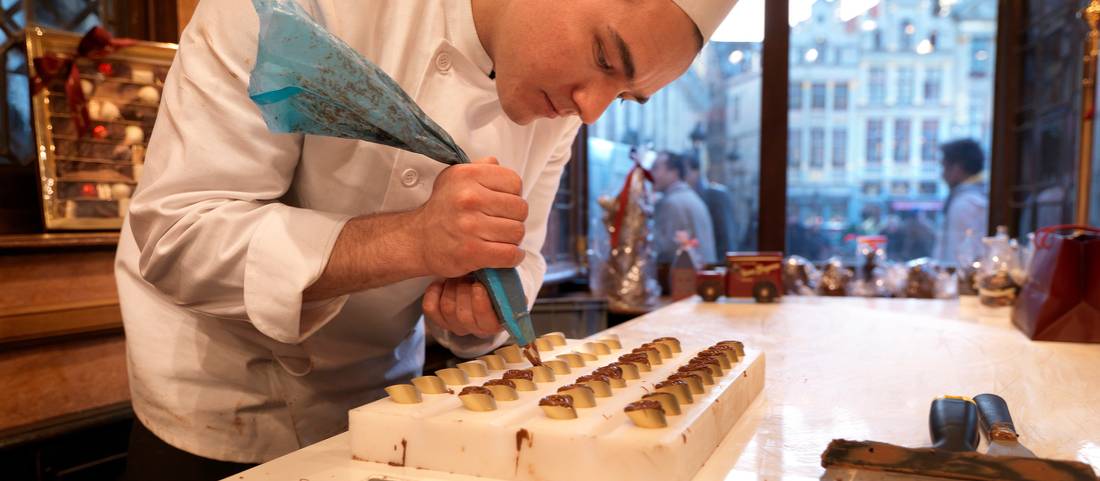

Future research could investigate:
1. Adaptive strategies for cocoa cultivation under changing climate conditions.
2. The role of digital tools in enhancing production efficiency and traceability.
3. Cross-cultural attitudes toward chocolate and their influence on consumption trends.