The Nutritional Profile of Flattened Rice: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Flattened rice, a light and flaky grain widely enjoyed across South Asia, has become a breakfast favorite for its quick preparation and gentle texture. This overview explores its nutritional highlights, possible advantages for everyday wellness, and a few practical cautions to keep in mind when adding it to regular meals.
Nutritional Snapshot of Flattened Rice
Carbohydrates
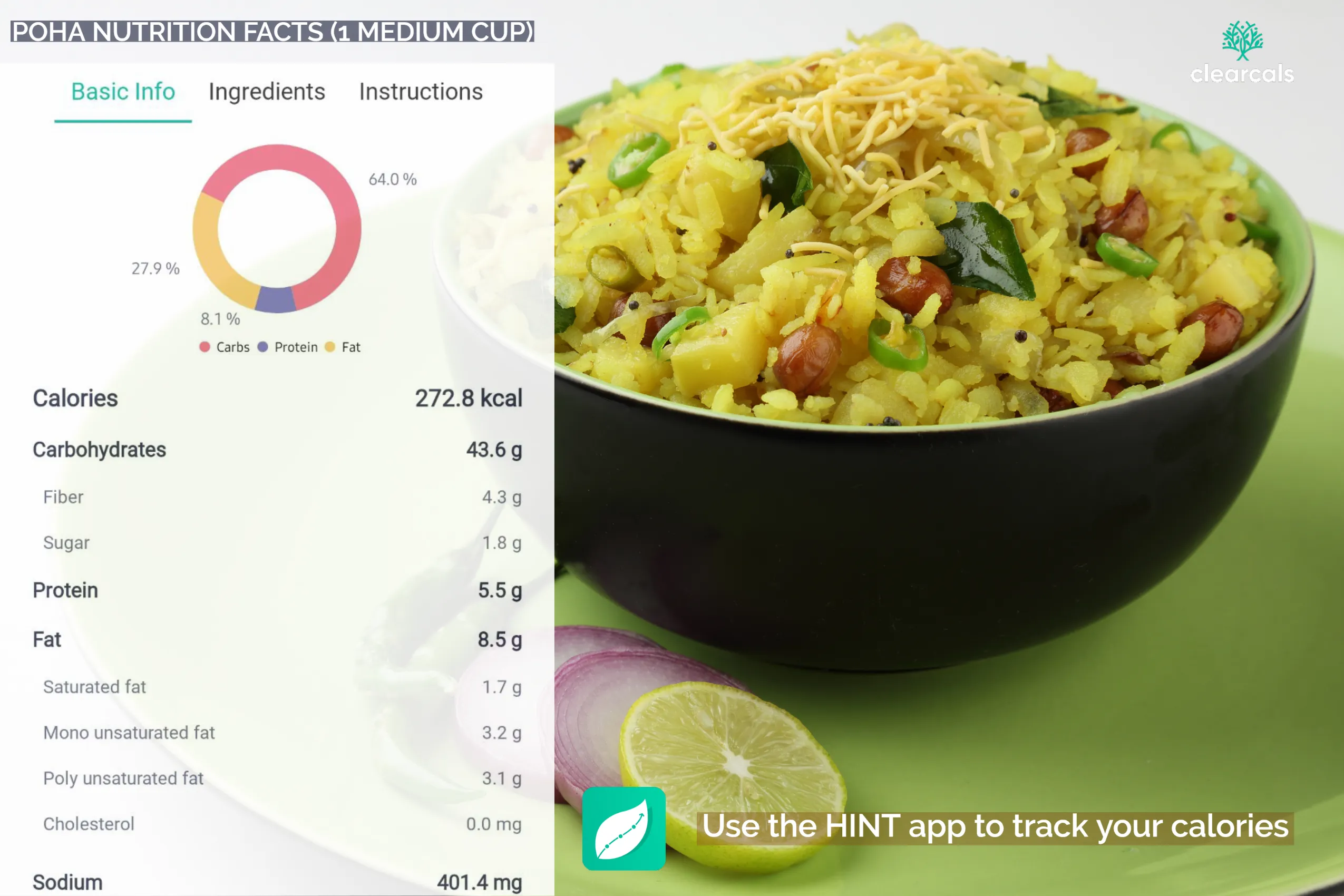
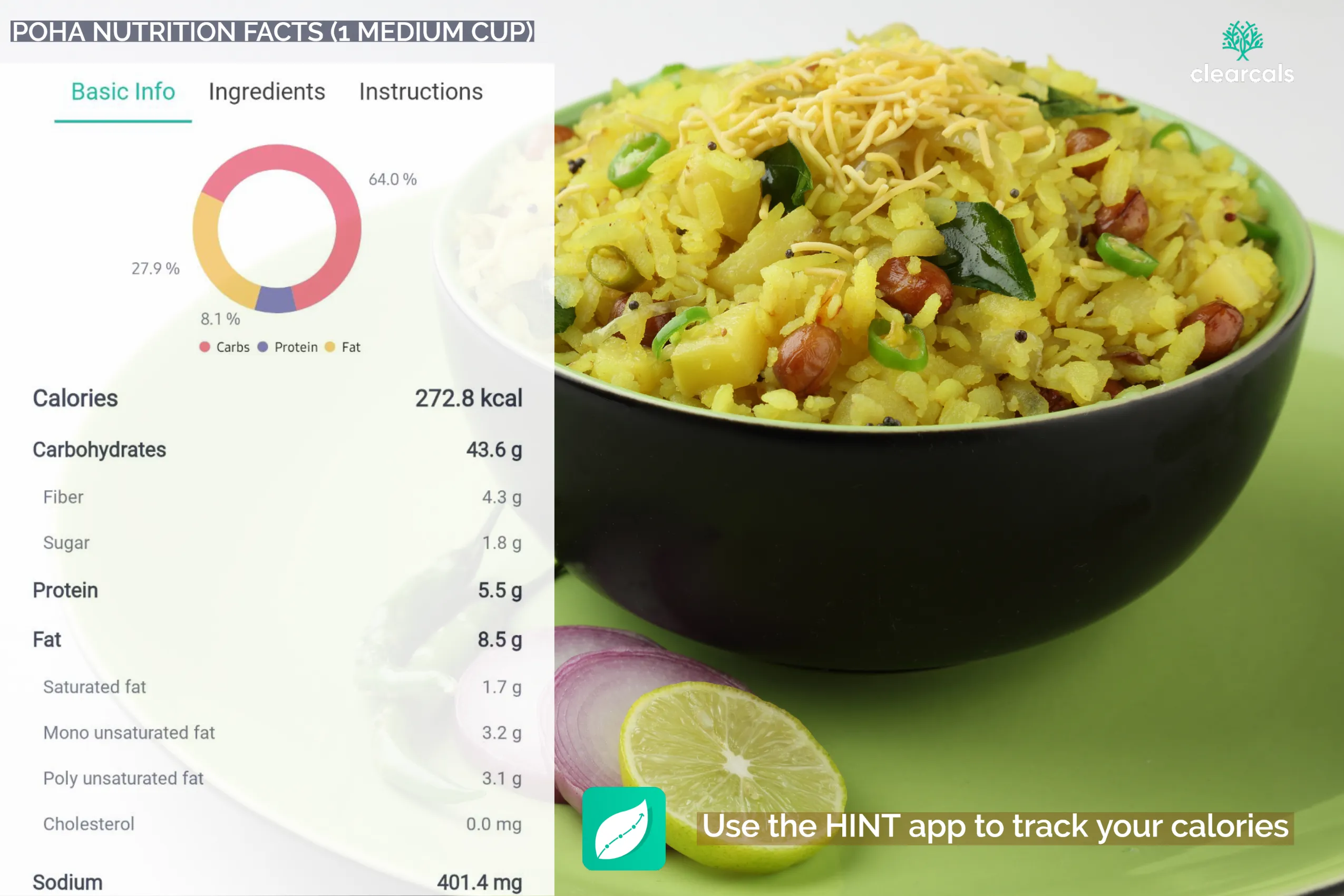
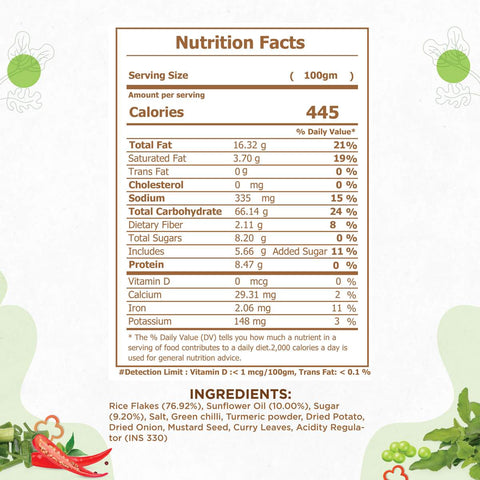
A standard serving of soaked and drained flattened rice supplies roughly 40 g of carbohydrates, translating to about 160 kcal. These carbs come mainly from readily available starches that provide an immediate but steady release of energy.
Proteins
Each serving offers around 4 g of plant protein. While modest, this amount complements other protein sources such as milk, yogurt, or legumes, helping support routine tissue maintenance.
Fats
The grain itself is naturally low in fat, carrying barely 1 g per serving, most of which is unsaturated. Final fat content depends on cooking style; sautéing in minimal oil keeps the dish heart-friendly.
Fiber
With close to 2 g of dietary fiber per serving, flattened rice contributes to daily roughage needs, encouraging smooth digestion and regularity.
Vitamins and Minerals

Flattened rice provides small but meaningful quantities of several micronutrients:
– B-vitamins, notably thiamine, riboflavin and niacin, which assist in converting food into usable energy and in maintaining healthy skin and nerves.
– Iron, supporting oxygen transport and overall vitality.
– Magnesium, important for muscle relaxation, bone strength and numerous enzymatic reactions.
Everyday Benefits

Weight Management
The combination of low calorie density and gentle fiber helps create a feeling of fullness, making it easier to control portion sizes at subsequent meals.
Digestive Comfort
Its soft texture and soluble fiber are kind to the stomach, often recommended during recovery from minor digestive upsets or for those who prefer lighter morning meals.
Heart Wellness

Minimal saturated fat, plus the grain’s inherent potassium and magnesium, fits well within diets aimed at maintaining healthy blood pressure and lipid profiles.
Bone Support
Trace minerals such as magnesium and phosphorus work alongside calcium-rich accompaniments—like a sprinkle of sesame seeds or a side of yogurt—to promote skeletal health.
Points to Consider
Allergies

Rice is generally hypoallergenic; nevertheless, anyone with known rice sensitivity should choose an alternative grain.
Cooking Style
Deep-frying or generous use of ghee, salt or sugar can quickly turn a light dish into a calorie-dense treat. Steaming, light tempering with minimal oil, or simply soaking and mixing with vegetables keeps the meal balanced.
Storage and Hygiene
Because the flakes are par-boiled and dried, they can absorb moisture quickly. Store in a sealed container in a cool cupboard, and always rinse or soak in clean water before use to avoid microbial growth.
Conclusion
Flattened rice offers a quick, gentle and nutrient-accommodating base for countless breakfast or snack ideas. When paired with vegetables, legumes or dairy and cooked with restraint, it supports energy levels, digestive ease and overall dietary variety without burdening the day’s calorie budget.
Future Research Directions
More controlled studies could clarify how regular intake affects glycemic response across different age groups and whether specific fermentation or soaking techniques further enhance mineral availability. Investigations into sustainable farming practices for the underlying rice crop would also align this traditional food with modern environmental goals.