The Rise and Impact of Plant-Based Cuisine: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
In recent years, meals built around plants have moved from niche to mainstream. Driven by wellness goals, ecological awareness, and ethical reflection, more diners are choosing dishes centered on vegetables, legumes, grains, nuts, and fruits. This overview traces the momentum of plant-forward eating, its influence on daily life, and the road ahead.

The Rise of Plant-Based Choices
Health Benefits
Balanced plant-focused plates tend to deliver generous fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients while keeping saturated fat in check. Regular enjoyment of such meals is linked to steadier weight, healthier cholesterol profiles, and lower incidence of several long-term illnesses.
Environmental Sustainability
Raising animals for food typically requires more land, water, and energy than growing crops for direct human consumption. By leaning on plants, eaters can lighten their personal environmental footprint and help conserve soil, forests, and freshwater reserves.

Ethical Considerations
Concerns about humane treatment have prompted many consumers to reduce or eliminate animal products. Choosing plant-based fare offers a way to align everyday decisions with compassion toward living creatures.
The Impact of Plant-Based Eating
Consumer Behavior
Supermarket shelves now hold oat milks, bean burgers, and cashew cheeses beside traditional staples. Restaurants highlight colorful grain bowls and meatless tacos, responding to a marked uptick in customer demand for vibrant, cruelty-free options.

Economic Impact
Producers of alternative proteins, dairy-free beverages, and egg-free dressings have seen rapid sales growth. Investment is flowing into research that improves texture, flavor, and affordability, signaling a durable market expansion.
Social Impact
Online communities swap recipes for lentil loafs and almond feta, while food influencers showcase rainbow Buddha bowls. Shared culinary creativity fosters a sense of belonging among those exploring plant-powered lifestyles.
Challenges and Future Prospects

Nutritional Concerns
Careful planning ensures adequate intake of vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fats. Fortified plant milks, seeds, leafy greens, and occasional supplements can cover potential gaps when meals are thoughtfully assembled.
Taste and Variety
Chefs and food scientists continue to refine smoking, fermenting, and seasoning techniques that lend umami depth to mushrooms, jackfruit, and tofu. Expanding global spice palettes keeps menus exciting and encourages long-term adoption.
Education and Awareness
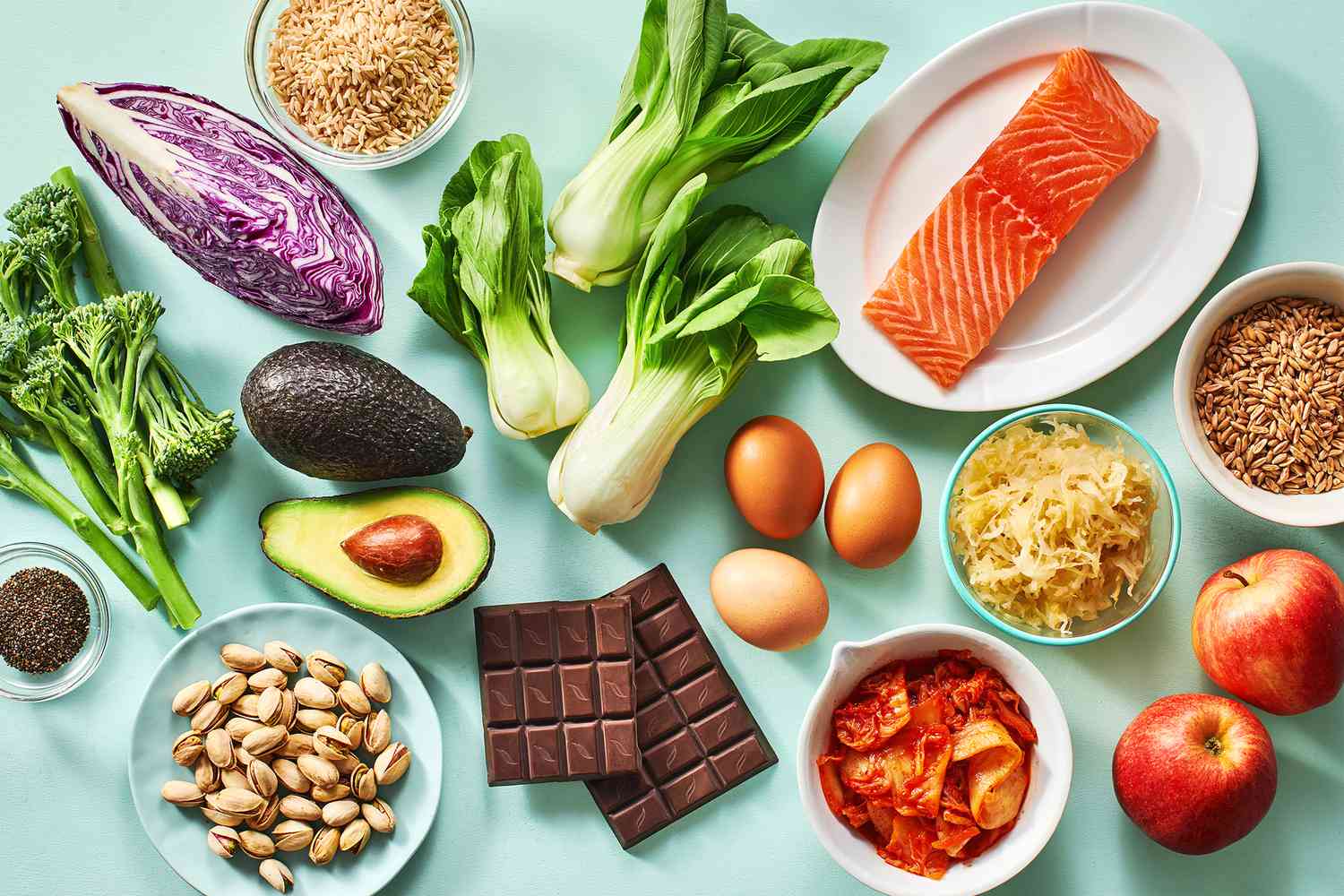

Clear, science-based guidance from nutritionists, culinary schools, and public-health campaigns equips home cooks and food-service professionals with the know-how to build satisfying, complete plant-based plates.
Conclusion
Plant-centered dining has taken root across cultures thanks to its triple appeal: personal health, planetary care, and ethical mindfulness. Continued innovation, transparent information, and inclusive food policies will nurture its evolution, helping communities enjoy meals that are kind to bodies, animals, and the Earth alike.
References
– Peer-reviewed journals on nutrition and sustainability

– Reports from international agricultural and health organizations
– Market analyses by leading food-industry research firms